The influence of heteroatom doping on the performance of carbon-based electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reactions
$ 13.50 · 4.6 (461) · In stock
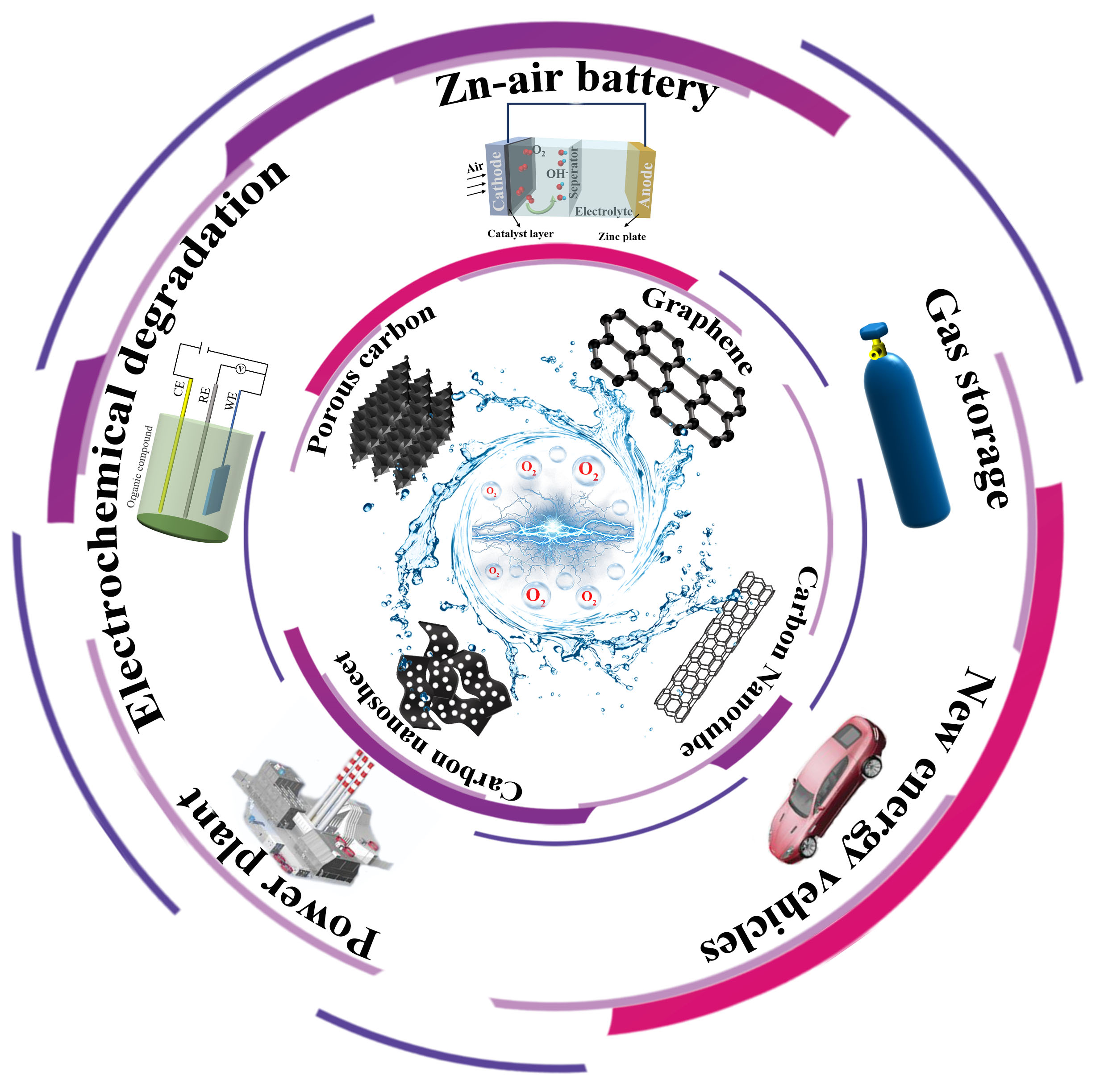
Various types of energy conversion and storage devices have been developed in recent years to tackle with the problems of the over-consumption of fossil fuels and the environmental pollution they cause. The oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is the key half-cell reaction of many energy conversion and storage devices. The influences of the heteroatom doping of metal-free carbon-based electrocatalysts with N, P, S or B and co-doping with N/P or N/S on their performance as OER electrocatalysts are reviewed. Doping methods to prepare metal-free carbon-based electrocatalysts are summarized, and problems that need to be solved are discussed and challenges for future research are proposed.

Research advances in earth-abundant-element-based electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction and oxygen reduction reaction

Cu-decorating on N, P-Codoped porous carbon derived from wheat straw as advanced catalysts for N-alkylation of amines with alcohols - ScienceDirect

Electronic optimization of heterostructured MoS2/Ni3S2 by P doping as bifunctional electrocatalysts for water splitting - ScienceDirect
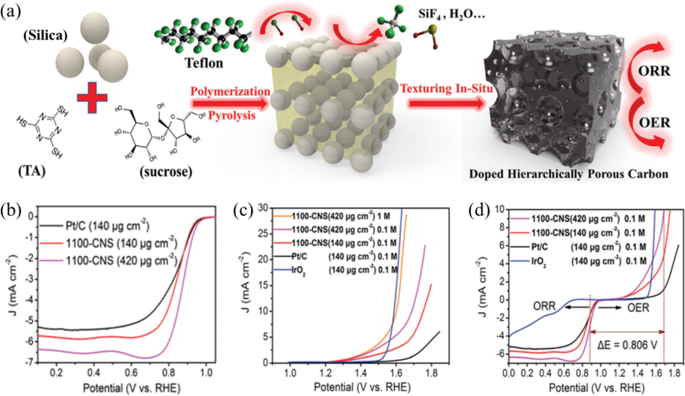
A review of oxygen reduction mechanisms for metal-free carbon-based electrocatalysts

PDF] Heteroatom-Doped Graphitic Carbon Catalysts for Efficient Electrocatalysis of Oxygen Reduction Reaction

Cu-decorating on N, P-Codoped porous carbon derived from wheat straw as advanced catalysts for N-alkylation of amines with alcohols - ScienceDirect

Unifying the origin of catalytic activities for carbon-based metal-free electrocatalysts - ScienceDirect

Heteroatom-doped carbon dots based catalysts for oxygen reduction reactions - ScienceDirect

Electronic optimization of heterostructured MoS2/Ni3S2 by P doping as bifunctional electrocatalysts for water splitting - ScienceDirect

Recent progress in increasing the electromagnetic wave absorption of carbon-based materials









